티스토리 뷰
C++와 C#의 문법적 차이에 대해 배웠다.
총 15개의 문제를 C++와 C#으로 풀어보았다.
VMware에서 C++컴파일러에 버그가 생겨 VScode로 대체하겠습니다...
[1] IO(input,output)
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int id; // 학번
char name[10]; // 이름(문자배열)
cout << "학번을 입력하세요: ";
cin >> id;
cout << "이름을 입력하세요: ";
cin >> name;
cout << "학번 : " << id << endl;
cout << "이름 : " << name << endl;
}캐릭터 배열을 만들어 값을 받아주었다. 그리고 단순하게 출력해주었다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B01_IO
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int id; // 학번
string name; // 이름(스트링=문자열)
Console.Write("학번을 입력하세요 : ");
id = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("이름을 입력하세요 : ");
name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("학번 : {0}", id);
Console.WriteLine("이름 : {0}", name);
}
}
}C#에서는 console.write(line)을 사용하여 입력시 string형식으로만 받기 때문에
다른 형식으로 파싱해주어야한다.
id = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());ex): integer형식으로 pharsing해 준 것을 볼 수 있다.

[2]사칙연산
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, y;
cout << "두개의 정수를 입력하세요: ";
cin >> x >> y;
cout << x << " + " << y << " = " << x + y << endl;
cout << x << " - " << y << " = " << x - y << endl;
cout << x << " * " << y << " = " << x * y << endl;
cout << x << " / " << y << " = " << x / y << endl;
cout << x << " % " << y << " = " << x % y << endl;
}사칙연산 코딩을 해보았다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B02_Arithmetic
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x, y;
Console.Write("첫번째 숫자를 입력하세요 : ");
x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("두번째 숫자를 입력하세요 : ");
y = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} = {2}", x, y, x+y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1} = {2}", x, y, x - y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} * {1} = {2}", x, y, x * y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1} = {2}", x, y, x / y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} % {1} = {2}", x, y, x % y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} % {1} = {2}", 3.14, 2.56, 3.14%2.56);
}
}
}double을 쓰지 않고 출력 문 내에서 소수점을 계산할 수 있다는점은 상당히 놀랍다.
Console.WriteLine("{0} % {1} = {2}", 3.14, 2.56, 3.14%2.56);
[3]관계연산자
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x, y;
cout << "두개의 정수를 입력하세요: ";
cin >> x >> y;
cout << x << " > " << y << " = " << (x > y) << endl;
cout << x << " >= " << y << " = " << (x >= y) << endl;
cout << x << " < " << y << " = " << (x < y) << endl;
cout << x << " <= " << y << " = " << (x <= y) << endl;
cout << x << " == " << y << " = " << (x == y) << endl;
cout << x << " != " << y << " = " << (x != y) << endl;
}모든 언어에서의 관계연산자는 6개이다. (같다,다르다,미만,초과,이하,이상)
{C#}
using System;
namespace B03_Relational
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x, y;
Console.WriteLine("x를 입력하세요 : ");
x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("y를 입력하세요 : ");
y = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("{0} > {1} = {2}", x, y, x > y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} >= {1} = {2}", x, y, x >= y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} < {1} = {2}", x, y, x < y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} <= {1} = {2}", x, y, x <= y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} == {1} = {2}", x, y, x == y);
Console.WriteLine("{0} != {1} = {2}", x, y, x != y);
}
}
}표기 방식도 C++와 같다.

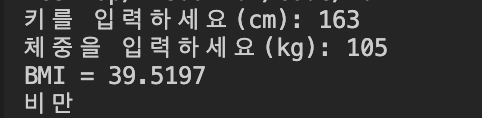
[4]BMI계산
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double height, weight;
cout << "키를 입력하세요(cm): ";
cin >> height;
cout << "체중을 입력하세요(kg): ";
cin >> weight;
height = height / 100; // height /= 100;
double bmi = weight / (height * height);
cout << "BMI = " << bmi << endl;
// 이제 판단을 하는 코딩
if (bmi < 20)
cout << "저체중\n";
else if (bmi < 25)
cout << "정상체중\n";
else if (bmi < 30)
cout << "경도비만\n";
else if (bmi < 40)
cout << "비만\n";
else
cout << "고도비만\n";
}체중과 키를 입력받아 BMI를 계산하고 비만정도를 출력하는 코드이다.
ifelse문의 반복보다는 switch/case문을 사용하는 것이 더 빠르다
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B04_BMI
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double height, weight;
Console.Write("키를 입력하세요(cm): ");
height = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("체중을 입력하세요(kg): ");
weight = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
height = height / 100; // height /= 100;
double bmi = weight / (height * height);
Console.WriteLine("BMI = {0}", bmi);
// 이제 판단을 하는 코딩
if (bmi < 20)
Console.WriteLine("저체중");
else if (bmi < 25)
Console.WriteLine("정상체중");
else if (bmi < 30)
Console.WriteLine("경도비만");
else if (bmi < 40)
Console.WriteLine("비만");
else
Console.WriteLine("고도비만");
}
}
}
height = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());소수점자리까지 계산하기 위해 double형식으로 파싱해준 것이 보인다.
[5]1~100까지
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int sum = 0; // 초기값 중요
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
sum += i; // sum = sum + i
cout << "1~100의 합 = " << sum << endl;
int evenSum = 0;
int oddSum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) // 짝수
evenSum += i;
else
oddSum += i;
}
cout << "1~100사이의 짝수의 합 = " << evenSum << endl;
cout << "1~100사이의 홀수의 합 = " << oddSum << endl;
double rSum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
rSum += 1.0 / i;
cout << "1~100의 역수의 합 = " << rSum << endl;
}1~100까지의 여러가지 값을 구하는 코드이다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B05_Loop
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
sum += i;
Console.WriteLine("1~100의 합 : {0}", sum);
int oddSum = 0;
int evenSum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
evenSum += i;
else
oddSum += i;
}
Console.WriteLine("1~100의 짝수의 합 = {0}", evenSum);
Console.WriteLine("1~100의 홀수의 합 = {0}", oddSum);
double rSum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
rSum += 1.0 / i;
Console.WriteLine("1~100의 역수의 합 = {0}", rSum);
}
}
}※주의사항
double rSum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
rSum += 1.0 / i;rSum을 double형태로 지정했지만 1.0 이 아닌 1 을 넣게되면 1을 i로 나눈 몫을 계속하여 더해주기 때문에
rSum += 0; 을 반복하는 것과 같다


[6] X ^ Y
{C++}
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int x, y;
cout << "두 정수 x와 y를 입력하세요: ";
cin >> x >> y;
int power = 1; // 비교, int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++) // y번 반복
power *= x;
cout << x << " ^ " << y << " = " << power << endl;
}X와 Y를 입력받은 후 X를 Y번 곱해주는 코드를 작성하였다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B06_Power
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("x를 입력하세요: ");
int x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("y를 입력하세요: ");
int y = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int power = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < y; i++)
power *= x;
Console.WriteLine("{0} ^ {1} = {2}", x, y, power);
}
}
}계산 방식은 같다
평소엔 cmath헤더의 pow()를 자주 사용한다.
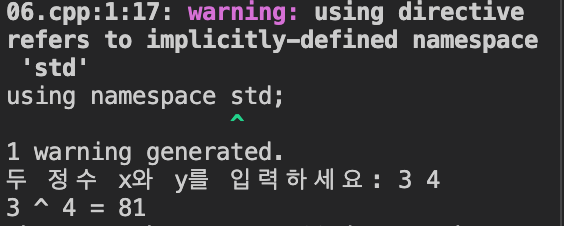
(이름공간 할당이 iostream선언보다 위에 있어서 경고가 뜬다.)
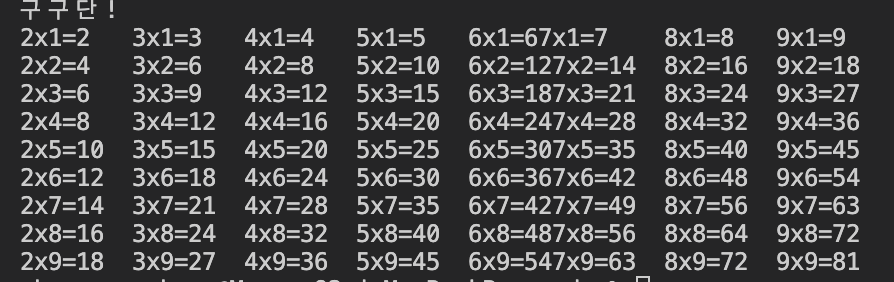
[7]구구단
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << "구구단!\n";
for (int y = 1; y <= 9; y++) {
for (int x = 2; x <= 9; x++)
cout << x << "x" << y << "=" << x * y << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}2중for문을 사용하여 81개의 값을 출력하는 코드이다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B07_Gugu
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int y = 1; y <= 9; y++)
{
for (int x = 2; x <= 9; x++)
{
Console.Write("{0}x{1}={2}\t", x, y, x * y);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}다양한 자료형을 한번에 출력하는 경우엔 C#의 console.write(line) 출력문이 C++의 cout 출력문보다 훨씬 효율적인 것 같다.
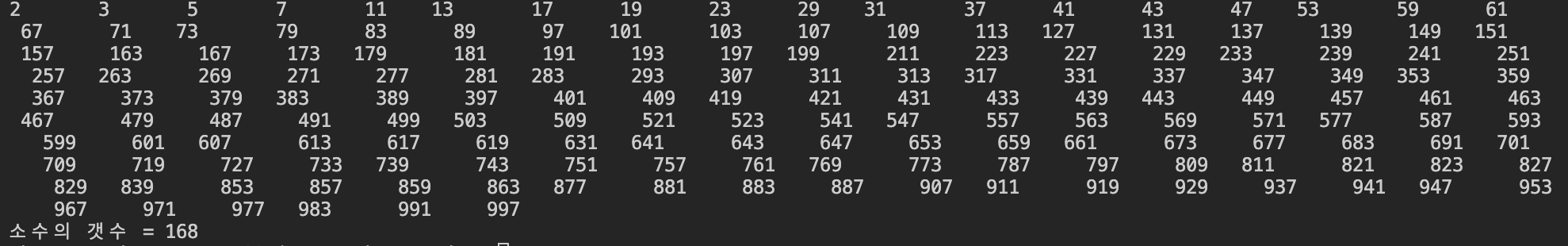
[8]소수의 개수
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int nPrime = 0;
int j;
for (int i = 2; i <= 1000; i++) {
for (j = 2; j <= i - 1; j++) {
if (i % j == 0) // 나누어지는 수, 소수가 아니다
break; // 반복문 하나를 빠져나간다
}
if (j == i) { // 소수라는 뜻이 된다
nPrime++;
cout << i << "\t";
}
}
cout << "\n소수의 갯수 = " << nPrime << endl;
}이 문제도 마찬가지로 이중for문을 사용하여 풀이했다.
1은 소수에 미포함이기 때문에 반복문은 2부터 시작
그러나, 브루트포스 스타일이라 굉장히 비효율적이다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B08_Prime
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// (1) 어떤 숫자가 소수인지를 판단하는 프로그램
//Console.Write("숫자하나를 입력하세요: ");
//int x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
//int i;
//for (i = 2; i < x; i++)
//{
// if (x % i == 0) // 소수가 아님
// break;
//}
//if (i == x)
// Console.WriteLine("소수입니다.");
//else
// Console.WriteLine("소수가 아닙니다");
// (2) 1000까지 소수를 출력하고 몇개인지를 출력하는 프로그램
int nPrime = 0;
for (int x = 2; x<=1000; x++)
{
int i;
for (i = 2; i < x; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0) // 소수가 아님
break;
}
if (i == x)
{
Console.Write("{0}\t", x);
nPrime++;
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("소수의 갯수 = {0}", nPrime);
}
}
}i를 x로 나눠 하나라도 나누어 떨어지면 break 후 i++로 반복해주는 코드이다.
소수를 구하는 코드로는 [에라토스테네스의 체]가 유명하다.
https://mooner92.tistory.com/4
[9]피라미드
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// 빈칸을 5-i개
for (int j = 0; j < 5 - i; j++)
cout << " ";
// 별표를 2*i-1개
for (int k = 0; k < 2 * i - 1; k++)
cout << "*";
cout << endl;
}
}매 칸 공백은 한칸씩 별은 두개씩 늘어나는 출력 코드이다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B09_Pyramid
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<=5-i; j++)
Console.Write(" ");
for(int j=1; j<=2*i-1; j++)
Console.Write("*");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}console.writeline()으로 cout <<endl; 을 대체하였다.
----5단트리 출력----

[10]랜덤한 수의 평균,최대,최소 구하기
{C++}
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(unsigned(time(0))); // 랜덤 시드(seed) 설정
// 배열에 저장
int a[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) // 중요
a[i] = rand();
// 출력
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
int min = a[0];
int max = a[0];
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sum += a[i];
if (min > a[i])
min = a[i];
else if (max < a[i])
max = a[i];
}
cout << "평균 = " << sum / 10.0 << endl;
cout << "최소 = " << min << endl;
cout << "최대 = " << max << endl;
}ctime 헤더를 포함해주고 srand함수로 랜덤한 인자를 뽑아내는데
unsigned를 사용하여 랜덤한 실수의 부호비트를 제거해줍니다.
srand(unsigned(time(0)));양수로만 구성된 배열 a의 원소들을 모두 출력해준 뒤 sum에는 배열a의 모든 원소값의 합을
min,max은 순차탐색으로 뽑아내줍니다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B10_Array
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Random r = new Random();
int[] a = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = r.Next(100); // 0~99사이의 랜덤값
//for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
// Console.WriteLine(a[i]);
// foreach 문
foreach(var x in a)
Console.WriteLine(x);
// 평균, 최소, 최대값을 계산
int sum = 0;
int min = a[0];
int max = a[0];
foreach(var x in a)
{
sum += x;
if (x < min)
min = x;
if (x > max)
max = x;
}
Console.WriteLine("평균 = {0}", sum/10.0);
Console.WriteLine("최소값 = {0}", min);
Console.WriteLine("최대값 = {0}", max);
}
}
}랜덤한 r을 new로 초기화해줍니다.
10칸짜리 배열 a를 생성하고
foreach문을 사용하여 배열을 빠르게 탐색해줍니다
foreach(var x in a)
Console.WriteLine(x);// 가변수 x가 a.length()-1만큼을 반복
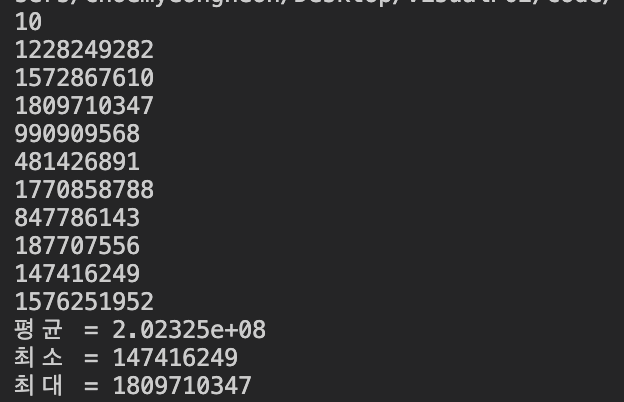
평균값을 sum+=원소 로 계산해버리는 바람에 값이 21.5억을 넘어 오버플로가 발생했다
파이썬이나 자바였다면 BigInt를 사용하여 해결 될 일이지만 C++에서는 일반적으로 string을 사용하여 문자열을 쪼개서 푼다....
[11](버블)정렬
{C++}
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
int main()
{
int a[10];
srand((unsigned)time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = rand() % 100;
cout << "Before Sorting : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
// 정렬하는 코드
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
for(int j=i+1; j<10; j++)
if (a[i] > a[j]) {
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
cout << "After Sorting : ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
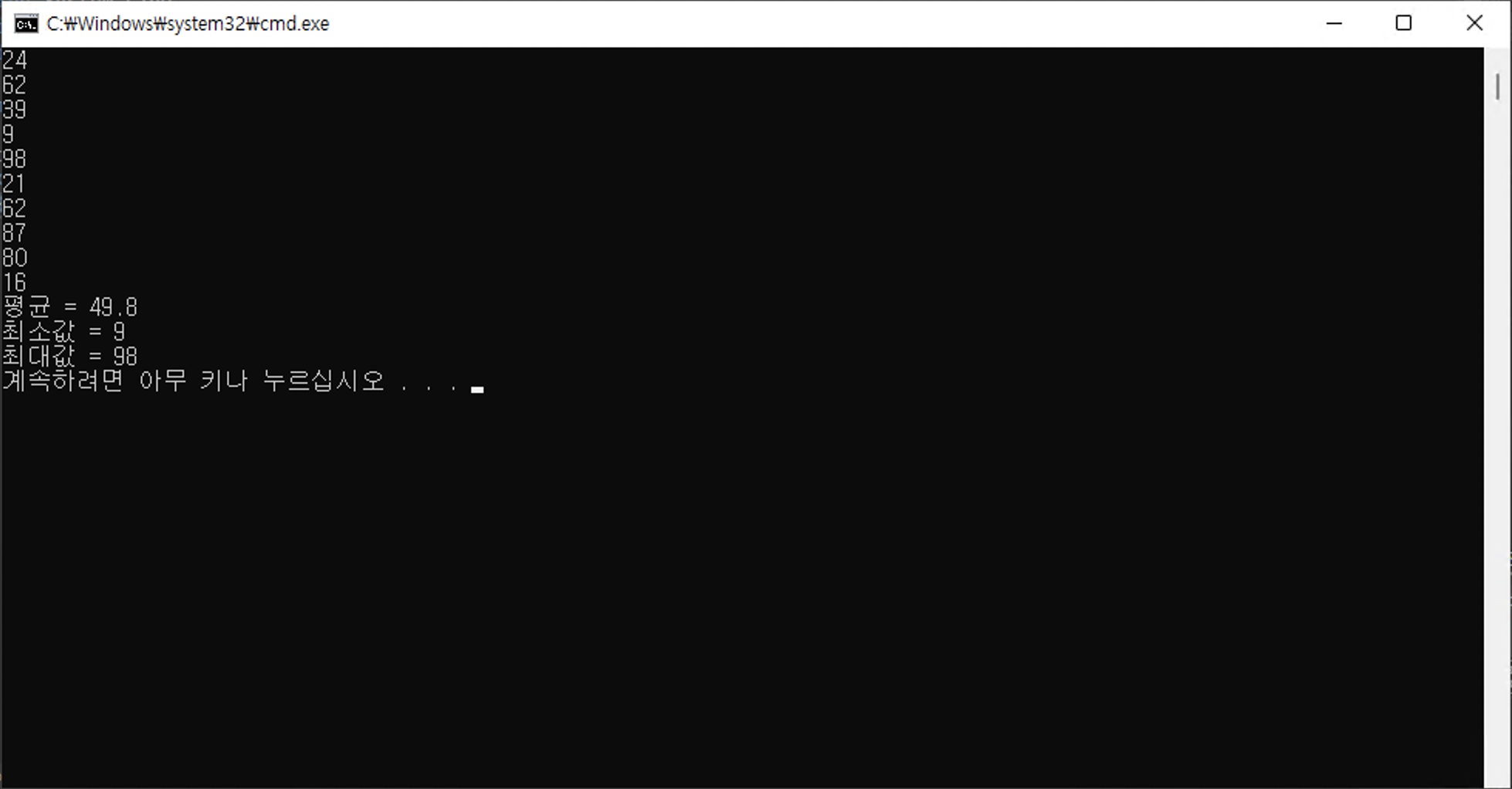
}100보다 작은 랜덤한 양수 10개를 받아 배열에 저장한 뒤
어떤 수와 그 뒷수의 대소를 비교하여 자리를 바꿔 정렬한다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B11_Sorting
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] a = new int[10];
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
a[i] = r.Next(100);
foreach (var v in a)
Console.Write("{0,5}", v);
Console.WriteLine();
for(int i=9; i>0; i--)
for(int j=0; j<i; j++)
if(a[j] > a[j+1])
{
int t = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = t;
}
foreach (var v in a)
Console.Write("{0,5}", v); // 첫번째 값을 5칸으로 출력
Console.WriteLine();
// 포맷 문자열, 교과서 10장에 설명
}
}
}대부분 C++과 비슷하지만
Console.Write("{0,5}", v)이 부분은 a[v]를 포매팅한 값을 5칸을 할당하여 오른쪽정렬을 한다.
Console.Write("{0,-5}", v)이렇게 -5가되면 왼쪽으로 정렬한다.

[12]큰 수
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Larger(int a, int b) {
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
int main()
{
int x, y, z;
cout << "세개의 값을 입력하세요 : ";
cin >> x >> y >> z;
//int max = Larger(x, y);
//max = Larger(max, z);
// 한줄로 만들자
int max = Larger(Larger(x, y), z);
cout << "최대값 = " << max << endl;
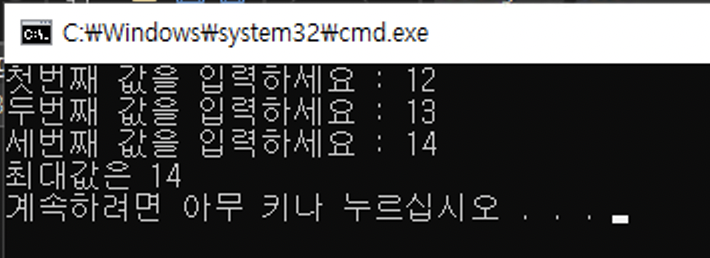
}처음으로 함수가 나왔다.
int형식의 값을 리턴하는 Larger함수를 만들어 이중으로 사용하여 최댓값을 뽑아내었다
Larger함수를 n겹으로 사용하여 n+1개 수의 최대값을 뽑아낼 수 있다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B12_Larger
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x, y, z;
Console.Write("첫번째 값을 입력하세요 : ");
x = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("두번째 값을 입력하세요 : ");
y = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("세번째 값을 입력하세요 : ");
z = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
//int max = Larger(x, y);
//max = Larger(max, z);
//int max = Larger(Larger(x, y), z);
Console.WriteLine("최대값은 {0}", Larger(Larger(x, y), z));
}
private static int Larger(int x, int y)
{
//if (x > y)
// return x;
//else
// return y;
// 조건연산자( ? : )
return (x > y) ? x : y;
}
}
}프라이빗형 정적 함수를 선언해주었고 값음 integer로 받는다.
C#에서는 삼항 연산자를 사용해주며. (조건) ? 참일때 : 거짓일때 로 깔끔하게 계산해주었다

[13]피라미드 함수
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Pyramid(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// 빈칸을 5-i개
for (int j = 0; j < n - i; j++)
cout << " ";
// 별표를 2*i-1개
for (int k = 0; k < 2 * i - 1; k++)
cout << "*";
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
Pyramid(3);
Pyramid(5);
Pyramid(7);
}9번의 피라미드 문제를 함수화한 것이다.
void함수를 사용하여 리턴값을 받지않고 출력만 할 수 있도록 만들었다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B13_PyramidMethod
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DrawPyramid(3);
DrawPyramid(5);
DrawPyramid(7);
}
private static void DrawPyramid(int n)
{
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
// 빈칸
for (int j = 1; j <= n - i; j++)
Console.Write(" ");
// 별표
for (int k = 1; k <= 2 * i - 1; k++)
Console.Write("*");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}C++과 상당히 흡사하다.


C#은 값을 3,11,16으로 바꾸어보았다.
[14]n!
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Factorial(int n) {
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
return Factorial(n - 1) * n;
}
int main()
{
cout << "n!을 구하기 위해 숫자 하나를 입력하세요 : ";
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << n << "! = " << Factorial(n) << endl;
}int형을 반환하는 Factorial 함수를 선언하여 1씩 작아지는 n을 계속 곱해줌
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B14_Factorial
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.Write("n!을 계산하고자 합니다. n을 입력하세요 : ");
int n = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact *= i;
Console.WriteLine("{0}! = {1}", n, fact);
Console.WriteLine("{0}! = {1}", n, Facto(n));
// 1~10까지의 팩토리얼을 구하시오
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++)
Console.WriteLine("{0, 2}! = {1,8}", i, Facto(i));
}
private static int Facto(int n)
{
if (n == 1)
return 1;
else
return Facto(n - 1) * n;
}
}
}Console.WriteLine("{0, 2}! = {1,8}", i, Facto(i));0번째 포맷(i)은 두칸을 주고 오른쪽정렬
1번째 포맷(facto(i))은 8칸을 주고 오른쪽 정렬

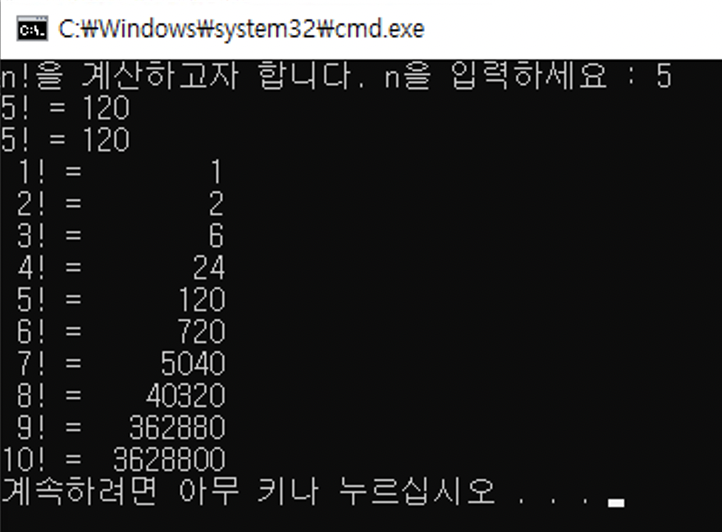
오른쪽으로 잘 정렬되어 나오는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
[15]하노이탑정렬(recursion)
{C++}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Hanoi(int n, char from, char via, char to)
{
// 재귀함수는 반드시 끝나는 조건이 있어야 한다
if (n == 1) {
cout << from << " -> " << to << endl;
}
else {
Hanoi(n - 1, from, to, via);
cout << from << " -> " << to << endl;
Hanoi(n - 1, via, from, to);
}
}
int main()
{
Hanoi(4, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
재귀를 사용하는 대표적인 문제이지만
재귀를 사용하여 경로를 출력하는 풀이는 오랜만이라 기억이 잘 안난다...
횟수만을 출력하는거라면 2P(n-1) +1을 사용하여
정리하면 2^n -1번이 나오게된다.
{C#}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace B15_Hanoi
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
HanoiTower(4, 'A', 'B', 'C');
// 교과서에서는 Hanoi(4, 'A', 'C', 'B')
}
private static void HanoiTower(int n, char from, char via, char to)
{
if(n == 1)
Console.WriteLine("{0}->{1}", from, to);
else
{
HanoiTower(n-1, from, to, via);
Console.WriteLine("{0}->{1}", from, to);
HanoiTower(n-1, via, from, to);
}
}
}
}순서를 바꿔주는 것이 어려울 수도 있지만
하노이탑은 세 단계로 분류할 수 있다.
1.n-1개의 원반을 경유지로 옮긴다.
2.n번째 원반을 목적지로 옮긴다.
3.경유지에 있던 n-1개의 원반을 목적지로 옮긴다.
여기서 매 번 경유지와 목적지 그리고 시작점의 위치가 달라지게된다(기준이되는 원판이 n번째판이냐 아니면 n-1개의 판들이냐에 따라)
그걸 공식화한게
HanoiTower(n-1, from, to, via);
Console.WriteLine("{0}->{1}", from, to);
HanoiTower(n-1, via, from, to);하노이 함수의 이 부분이다.

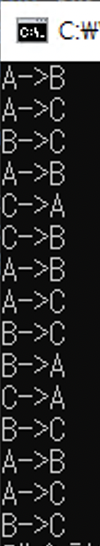
긴 글 읽..
'VS-02분반수업' 카테고리의 다른 글
| VSP02(22-03-30) (0) | 2022.04.06 |
|---|---|
| VSP02(2022-03-23) (0) | 2022.03.31 |
| VSP02(2022-03-16) (0) | 2022.03.23 |
| VSP02(2022-03-18) (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| VSP02(2022-03-02) (0) | 2022.03.02 |
